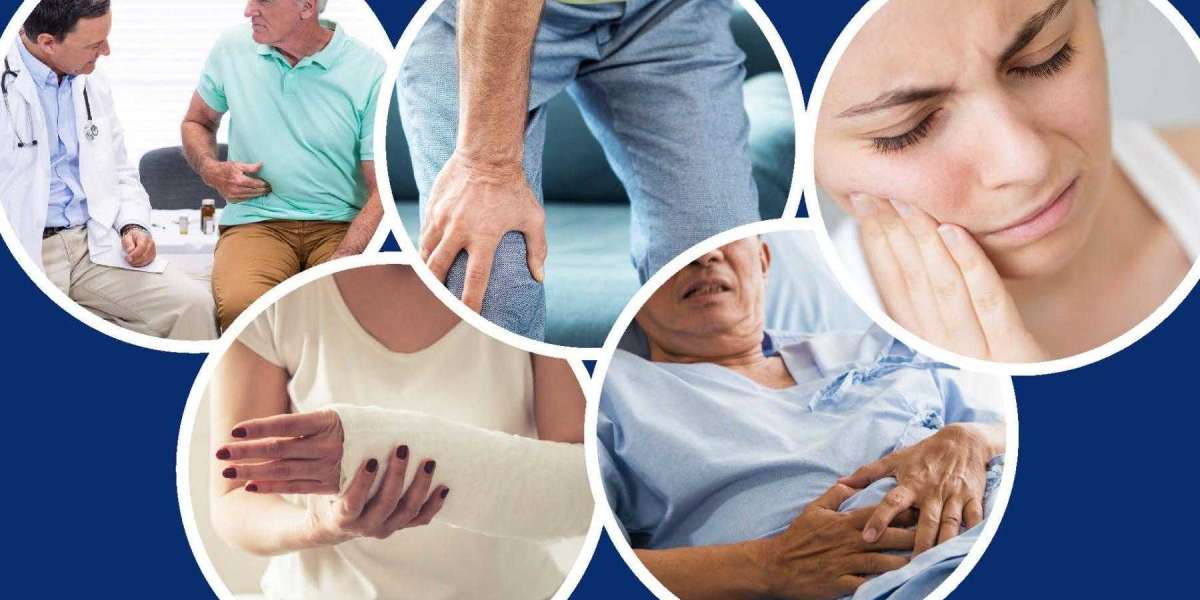
Neuropathic pain, characterized by its persistent and often debilitating nature, affects millions worldwide. For those suffering from this condition, finding effective relief is paramount to improving quality of life. One of the prominent medications prescribed for neuropathic pain is Pregabalin 100 mg—commonly known by its brand name Lyrica. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into what Pregabalin 100 mg is, how it works, its benefits, potential side effects, and considerations for use in 2024.
Understanding Pregabalin 100 mg
Pregabalin belongs to a class of medications known as anticonvulsants. Initially approved by the FDA in 2004, it has since become a cornerstone in the treatment of neuropathic pain, diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, and fibromyalgia. The 100 mg dosage is a common starting point for many patients, with adjustments made based on individual response and severity of symptoms.
Mechanism of Action
Pregabalin exerts its therapeutic effects by binding to calcium channels in the central nervous system. This binding reduces the release of neurotransmitters such as glutamate, norepinephrine, and substance P, which are involved in transmitting pain signals. By modulating these neurotransmitters, Pregabalin 100 mg helps to dampen the abnormal electrical activity in damaged nerves, thereby alleviating neuropathic pain.
Benefits of Pregabalin 100 mg
The efficacy of Pregabalin 100 mg in managing neuropathic pain has been well-documented through clinical trials and real-world use. Patients often report significant improvements in pain intensity, sleep quality, and overall functioning. Unlike opioids, Pregabalin is not associated with the same risks of tolerance, dependence, or addiction, making it a safer long-term option for chronic pain management.
Potential Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, Pregabalin can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, weight gain, and dry mouth. These effects are usually mild to moderate and tend to diminish over time as the body adjusts to the medication. Serious side effects such as allergic reactions or mood changes are rare but should be promptly reported to a healthcare provider.
Considerations for Use
Before starting Pregabalin 100 mg, it is crucial for healthcare providers to assess the patient’s medical history, existing medications, and any potential drug interactions. Pregabalin may interact with certain medications or exacerbate certain health conditions, such as kidney problems. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also consult their healthcare provider before using this medication.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Pregabalin 100 mg remains a cornerstone treatment for neuropathic pain in 2024, offering effective relief with a favorable safety profile for many patients. As with any medication, individual responses may vary, and close monitoring by healthcare providers is essential to ensure optimal outcomes. By understanding how Pregabalin works, its benefits, potential side effects, and considerations for use, patients and healthcare professionals alike can make informed decisions regarding its role in managing neuropathic pain.